A) They cause the insertion or deletion of a single amino acid from the polypeptide chain.
B) They create a premature stop codon at the site of mutation.
C) They change the amino acid sequence downstream from the mutant site.
D) They are known risk factors in most forms of cancer, including breast and colon cancer.
E) They are known risk factors in breast cancer, but not colon cancer.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the standard genetic code (Table 4.1, shown below) , what fraction of codons are nonsense codons? 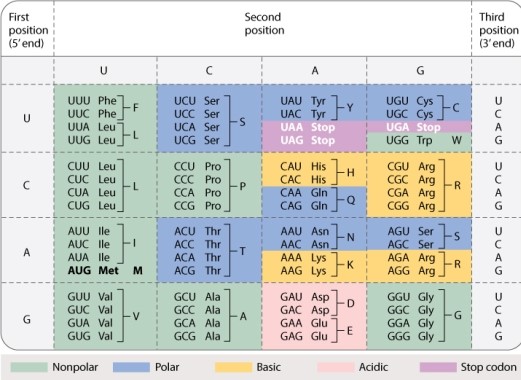
A) 1/64
B) 2/64
C) 3/64
D) 4/64
E) 5/64
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The definition of mutation is "any heritable change in the genetic material." The qualifier "heritable" is necessary because:
A) most changes in the genetic material are harmful to the organism.
B) changes in the genetic material occur at random along the genome.
C) changes in the genetic material occur without regard to the needs of the organism.
D) most changes in the genetic material are repaired soon after they occur.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_____ is the process where new genes evolve from duplicates of old ones.
A) Duplication and divergence
B) Inversion
C) Reciprocal translocation
D) Deletion
E) Centromere dosage
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the standard genetic code, how many amino acids have codons that allow synonymous mutations in the first position?
A) 0
B) 2
C) 8
D) 16
E) 20
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Depurination is a type of mutation where a purine base is lost, but the DNA backbone remains intact. Which of the following are likely to occur as a result of depurination?
A) An incorrect base can be incorporated in the next round of replication.
B) A deletion will occur, and there will be an overall loss of a base to the DNA strand.
C) Repair enzymes will recognize the error and replace the defective nucleotide.
D) An incorrect base can be incorporated in the next round of replication, and repair enzymes will recognize the error and replace the defective nucleotide.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The accompanying diagram shows three gene duplication events that gave rise to a gene family consisting of four sequences X1- X4. A researcher sequences the genes in two related species and discovers that each species has two copies. One species has copies X1 and X2, and the other has copies X3 and X4. The sequence of X1 is very close to that of X2, and the sequence of X3 is very close to that of X4; however, the (X1, X2) pair is quite dissimilar from the (X3, X4) pair. The most likely interpretation of this pattern is that speciation took place in the interval labeled: 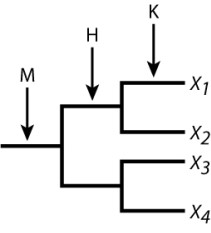
A) M)
B) H)
C) K)
D) None of the answer options is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Incorrectly repaired double-stranded breaks in DNA can produce:
A) duplications.
B) deletions.
C) inversions.
D) translocations.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Only germ-line mutations are transmitted to the progeny.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Any DNA "damage" is considered to be a mutation, even if it is immediately corrected by the action of DNA polymerase.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following enzymes is responsible for initiating certain types of base excision repair?
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) AP endonuclease
D) DNA uracil glycosylase
E) None of the other answer options is correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Loss of a pyrimidine base is one of the most common types of DNA damage.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each curve in the graph below shows the proportion of amino acid differences between a protein in two species that diverged from a common ancestral species. Which curve represents what would be expected if the protein were evolving according to a molecular clock? 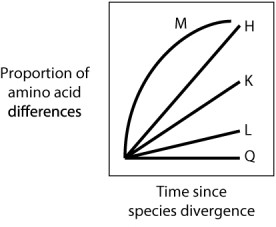
A) curve M
B) curve H
C) curve K
D) curve L
E) curve Q
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sickle-cell anemia results from what type of mutation?
A) silent
B) missense
C) nonsense
D) frameshift
E) base pair deletion
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the tryptophan codon 5-UGG-3 in the standard genetic code (Table 4.1, shown below) . Can a single base change in this codon create a synonymous mutation? Can a single base change in this codon create a nonsense codon? 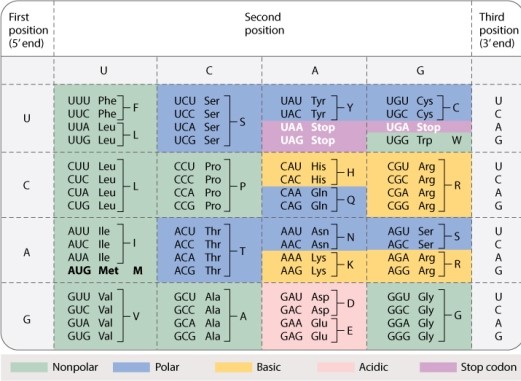
A) yes; yes
B) yes; no
C) no; yes
D) no; no
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Any deviation in normal gene dosage is lethal.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nonsense mutation:
A) changes the identity of one amino acid in a polypeptide chain.
B) shifts the reading frame of a messenger RNA.
C) is usually due to a nucleotide substitution in the third position of a codon.
D) changes a codon for an amino acid into a codon for chain termination.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutation consisting of a single-nucleotide deletion creates a frameshift in a long open reading frame. In the shifted reading frame, what is the expected average number of codons before a nonsense codon is encountered? (Round any fraction to the nearest whole number.)
A) 11
B) 13
C) 16
D) 21
E) 32
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do RNA viruses and retroviruses have such high rates of mutation?
A) because RNA polymerase is an unstable enzyme
B) because RNA viruses and retroviruses initially cause host-cell mutations during replication
C) because RNA is more fragile than DNA and is therefore more likely to be damaged
D) because viral polymerases lack a proofreading mechanism
E) because viral RNA can form stem-and-loop structures
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme _____ repairs breaks in the DNA sugar-phosphate backbone.
A) DNA ligase
B) DNA polymerase
C) AP endonuclease
D) uracyl glycosylase
E) None of the other answer options is correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 165
Related Exams