A) increases
B) decreases
C) increases at high temperature, decreases at low
D) decreases at high temperature, increases at low
E) stays the same
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram shows three isotherms for an ideal gas, with T3-T2 the same as T2-T1.It also shows five thermodynamic processes carried out on the gas.Rank the processes in order of the change in the internal energy of the gas, least to greatest. 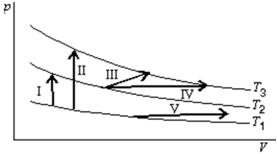
A) I, II, III, IV, V
B) V; then I, III and IV tied; then II
C) V; I; then III, and IV tied; then II
D) II; then I, III and IV tied; then V
E) II; I; then III, IV, and V tied
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An isothermal process for an ideal gas is represented on a p-V diagram by:
A) a horizontal line
B) a vertical line
C) a portion of an ellipse
D) a portion of a parabola
E) a hyperbola
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The heat capacity at constant volume and the heat capacity at constant pressure have different values because:
A) heat increases the internal energy at constant volume but not at constant pressure
B) heat increases the internal energy at constant pressure but not at constant volume
C) the system does work at constant volume but not at constant pressure
D) the system does work at constant pressure but not at constant volume
E) the system does more work at constant volume than at constant pressure
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pressure of an ideal gas of diatomic molecules is doubled by halving the volume.The ratio of the new internal energy to the old, both measured relative to the internal energy at 0 K, is:
A) 1/4
B) 1/2
C) 1
D) 2
E) 4
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
TV is constant for an ideal gas undergoing an adiabatic process, where is the ratio of heat capacities Cp/Cv.This is a direct consequence of:
A) the zeroth law of thermodynamics alone
B) the zeroth law and the ideal gas equation of state
C) the first law of thermodynamics alone
D) the ideal gas equation of state alone
E) the first law and the equation of state
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxygen (molar mass = 32 g) occupies a volume of 12 liters when its temperature is 20°C and its pressure is 1 atm.Using R = 0.082 liter.atm/mole.K, calculate the mass of the oxygen:
A) 6.4 g
B) 11 g
C) 16 g
D) 32 g
E) 64 g
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a slow adiabatic expansion of a gas:
A) the pressure remains constant
B) energy is added as heat
C) work is done on the gas
D) no energy enters or leaves as heat
E) the temperature is constant
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A real gas undergoes a process which can be represented as a curve on a p-V diagram.This curve is an isotherm if:
A) the volume of the gas does not change
B) the temperature of the gas does not change
C) the pressure of the gas does not change
D) the gas does no work on its environment
E) the gas exchanges no heat with its environment
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Air enters a hot-air furnace at 7°C and leaves at 77°C.If the pressure does not change each entering cubic meter of air expands to:
A) 0.80 m3
B) 1.25 m3
C) 1.9 m3
D) 7.0 m3
E) 11 m3
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas, which of the following is NOT true?
A) ![]() = constant
= constant
B) pV = nRT
C) ![]() = constant
= constant
D) W = - V pdV
E) pV = constant
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In using the ideal gas law, the temperature T must be measured in:
A) Celsius
B) Kelvin
C) Fahrenheit
D) either Celsius or Kelvin
E) any units as long as the correct values of k or R are used
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a given change in temperature, the change in the internal energy of an ideal gas:
A) also depends on the change in pressure
B) also depends on the change in volume
C) depends on whether the process is adiabatic or not
D) depends on whether the process occurs at constant pressure or not
E) can be calculated assuming the volume is constant
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The specific heat of a polyatomic gas is greater than the specific heat of a monatomic gas because:
A) the polyatomic gas does more positive work when energy is absorbed as heat
B) the monatomic gas does more positive work when energy is absorbed as heat
C) the energy absorbed by the polyatomic gas is split among more degrees of freedom
D) the pressure is greater in the diatomic gas
E) a monatomic gas cannot hold as much heat
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pressure of an ideal gas is doubled during a process in which the energy given up as heat by the gas equals the work done on the gas.As a result, the volume is:
A) doubled
B) halved
C) unchanged
D) need more information to answer
E) nonsense, the process is impossible
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two ideal monatomic gases are in thermal equilibrium with each other.Gas A is composed of molecules with mass m while gas B is composed of molecules with mass 4m.The ratio of the average molecular speeds vA/vB is:
A) 1/4
B) 1/2
C) 1
D) 2
E) 4
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ideal monatomic gas A is composed of molecules with mass m while ideal monatomic gas B is composed of molecules with mass 4m.The average molecular energies are the same if the ratio of the temperatures TA/TB is:
A) 1/4
B) 1/2
C) 1
D) 2
E) 4
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an adiabatic expansion,
A) the temperature of the gas does not change.
B) the gas does work on the environment, and the internal energy of the gas decreases.
C) the environment does work on the gas, and the internal energy of the gas increases.
D) the volume of the gas does not change.
E) the pressure of the gas does not change.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The energy absorbed as heat by an ideal gas for an isothermal process equals:
A) the work done by the gas
B) the work done on the gas
C) the change in the internal energy of the gas
D) the negative of the change in internal energy of the gas
E) zero since the process is isothermal
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the temperature T of an ideal gas is increased at constant pressure the mean free path:
A) decreases in proportion to 1/T
B) decreases in proportion to 1/T2
C) increases in proportion to T
D) decreases in proportion to T2
E) does not change
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 114
Related Exams