A) The bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach to estimating the cost of common equity involves adding a risk premium to the interest rate on the company's own long-term bonds.The size of the risk premium for bonds with different ratings is published daily in The Wall Street Journal or is available online.
B) The WACC is calculated using a before-tax cost for debt that is equal to the interest rate that must be paid on new debt,along with the after-tax costs for common stock and for preferred stock if it is used.
C) An increase in the risk-free rate is likely to reduce the marginal costs of both debt and equity.
D) The relevant WACC can change depending on the amount of funds a firm raises during a given year.Moreover,the WACC at each level of funds raised is a weighted average of the marginal costs of each capital component,with the weights based on the firm's target capital structure.
E) Beta measures market risk,which is generally the most relevant risk measure for a publicly-owned firm that seeks to maximize its intrinsic value.However,this is not true unless all of the firm's stockholders are well diversified.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Schalheim Sisters Inc.has always paid out all of its earnings as dividends,hence the firm has no retained earnings.This same situation is expected to persist in the future.The company uses the CAPM to calculate its cost of equity,its target capital structure consists of common stock,preferred stock,and debt.Which of the following events would REDUCE its WACC?
A) The market risk premium declines.
B) The flotation costs associated with issuing new common stock increase.
C) The company's beta increases.
D) Expected inflation increases.
E) The flotation costs associated with issuing preferred stock increase.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that Kish Inc.hired you as a consultant to help estimate its cost of capital.You have obtained the following data: D0 = $0.90;P0 = $47.50;and g = 7.00% (constant) .Based on the DCF approach,what is the cost of equity from retained earnings? Do not round your intermediate calculations.
A) 8.85%
B) 10.38%
C) 10.02%
D) 8.03%
E) 9.03%
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The cost of capital used to evaluate a project should be the cost of the specific type of financing used to fund that project,i.e. ,it is the after-tax cost of debt if debt is to be used to finance the project or the cost of equity if the project will be financed with equity.
B) The after-tax cost of debt that should be used as the component cost when calculating the WACC is the average after-tax cost of all the firm's outstanding debt.
C) Suppose some of a publicly-traded firm's stockholders are not diversified;they hold only the one firm's stock.In this case,the CAPM approach will result in an estimated cost of equity that is too low in the sense that if it is used in capital budgeting,projects will be accepted that will reduce the firm's intrinsic value.
D) The cost of equity is generally harder to measure than the cost of debt because there is no stated,contractual cost number on which to base the cost of equity.
E) The bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach is the most sophisticated and objective method for estimating a firm's cost of equity capital.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Norris Enterprises,an all-equity firm,has a beta of 2.0.The chief financial officer is evaluating a project with an expected return of 14%,before any risk adjustment.The risk-free rate is 5%,and the market risk premium is 4%.The project being evaluated is riskier than the firm's average project,in terms of both its beta risk and its total risk.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The project should definitely be accepted because its expected return (before any risk adjustments) is greater than its required return.
B) The project should definitely be rejected because its expected return (before risk adjustment) is less than its required return.
C) Riskier-than-average projects should have their expected returns increased to reflect their higher risk.Clearly,this would make the project acceptable regardless of the amount of the adjustment.
D) The accept/reject decision depends on the firm's risk-adjustment policy.If Norris' policy is to increase the required return on a riskier-than-average project to 3% over rs,then it should reject the project.
E) Capital budgeting projects should be evaluated solely on the basis of their total risk.Thus,insufficient information has been provided to make the accept/reject decision.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The component cost of preferred stock is expressed as rp(1 - T) .This follows because preferred stock dividends are treated as fixed charges,and as such they can be deducted by the issuer for tax purposes.
B) A cost should be assigned to retained earnings due to the opportunity cost principle,which refers to the fact that the firm's stockholders would themselves expect to earn a return on earnings that were paid out rather than retained and reinvested.
C) No cost should be assigned to retained earnings because the firm does not have to pay anything to raise them.They are generated as cash flows by operating assets that were raised in the past,hence they are "free."
D) Suppose a firm has been losing money and thus is not paying taxes,and this situation is expected to persist into the foreseeable future.In this case,the firm's before-tax and after-tax costs of debt for purposes of calculating the WACC will both be equal to the interest rate on the firm's currently outstanding debt,provided that debt was issued during the past 5 years.
E) If a firm has enough retained earnings to fund its capital budget for the coming year,then there is no need to estimate either a cost of equity or a WACC.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a capital component when calculating the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for use in capital budgeting?
A) Long-term debt.
B) Accounts payable.
C) Retained earnings.
D) Common stock.
E) Preferred stock.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You were hired as a consultant to Giambono Company,whose target capital structure is 40% debt,15% preferred,and 45% common equity.The after-tax cost of debt is 6.00%,the cost of preferred is 7.50%,and the cost of retained earnings is 12.00%.The firm will not be issuing any new stock.What is its WACC?
A) 8.93%
B) 7.59%
C) 6.96%
D) 7.68%
E) 6.69%
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The cost of debt is equal to one minus the marginal tax rate multiplied by the interest rate on new debt.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When estimating the cost of equity by use of the DCF method,the single biggest potential problem is to determine the growth rate that investors use when they estimate a stock's expected future rate of return.This problem leaves us unsure of the true value of rs.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Safeco Company and Risco Inc are identical in size and capital structure.However,the riskiness of their assets and cash flows are somewhat different,resulting in Safeco having a WACC of 10% and Risco a WACC of 12%.Safeco is considering Project X,which has an IRR of 10.5% and is of the same risk as a typical Safeco project.Risco is considering Project Y,which has an IRR of 11.5% and is of the same risk as a typical Risco project. Now assume that the two companies merge and form a new company,Safeco/Risco Inc.Moreover,the new company's market risk is an average of the pre-merger companies' market risks,and the merger has no impact on either the cash flows or the risks of Projects X and Y.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If the firm evaluates these projects and all other projects at the new overall corporate WACC,it will probably become riskier over time.
B) If evaluated using the correct post-merger WACC,Project X would have a negative NPV.
C) After the merger,Safeco/Risco would have a corporate WACC of 11%.Therefore,it should reject Project X but accept Project Y.
D) Safeco/Risco's WACC,as a result of the merger,would be 10%.
E) After the merger,Safeco/Risco should select Project Y but reject Project X.If the firm does this,its corporate WACC will fall to 10.5%.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Since 70% of the preferred dividends received by a corporation are excluded from taxable income,the component cost of equity for a company that pays half of its earnings out as common dividends and half as preferred dividends should,theoretically,be Cost of equity = rs(0.30)(0.50)+ rps(1 - T)(0.70)(0.50).
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You were recently hired by Scheuer Media Inc.to estimate its cost of capital.You obtained the following data: D1 = $1.75;P0 = $115.00;g = 7.00% (constant) ;and F = 5.00%.What is the cost of equity raised by selling new common stock?
A) 9.98%
B) 10.49%
C) 8.52%
D) 8.60%
E) 7.05%
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In general,firms should use their weighted average cost of capital (WACC)to evaluate capital budgeting projects because most projects are funded with general corporate funds,which come from a variety of sources.However,if the firm plans to use only debt or only equity to fund a particular project,it should use the after-tax cost of that specific type of capital to evaluate that project.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) In the WACC calculation,we must adjust the cost of preferred stock (the market yield) to reflect the fact that 70% of the dividends received by corporate investors are excluded from their taxable income.
B) We should use historical measures of the component costs from prior financings that are still outstanding when estimating a company's WACC for capital budgeting purposes.
C) The cost of new equity (re) could possibly be lower than the cost of retained earnings (rs) if the market risk premium,risk-free rate,and the company's beta all decline by a sufficiently large amount.
D) Its cost of retained earnings is the rate of return stockholders require on a firm's common stock.
E) The component cost of preferred stock is expressed as rp(1 - T) ,because preferred stock dividends are treated as fixed charges,similar to the treatment of interest on debt.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A.Butcher Timber Company hired your consulting firm to help them estimate the cost of equity.The yield on the firm's bonds is 6.75%,and your firm's economists believe that the cost of equity can be estimated using a risk premium of 3.85% over a firm's own cost of debt.What is an estimate of the firm's cost of equity from retained earnings?
A) 10.60%
B) 9.54%
C) 12.19%
D) 12.51%
E) 7.95%
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The text identifies three methods for estimating the cost of common stock from retained earnings: the CAPM method,the DCF method,and the bond-yield-plus-risk-premium method.However,only the CAPM method always provides an accurate and reliable estimate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose you are the president of a small,publicly-traded corporation.Since you believe that your firm's stock price is temporarily depressed,all additional capital funds required during the current year will be raised using debt.In this case,the appropriate marginal cost of capital for use in capital budgeting during the current year is the after-tax cost of debt.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since debt capital can cause a company to go bankrupt but equity capital cannot,debt is riskier than equity,and thus the after-tax cost of debt is always greater than the cost of equity.
B) The tax-adjusted cost of debt is always greater than the interest rate on debt,provided the company does in fact pay taxes.
C) If a company assigns the same cost of capital to all of its projects regardless of each project's risk,then the company is likely to reject some safe projects that it actually should accept and to accept some risky projects that it should reject.
D) Because no flotation costs are required to obtain capital as retained earnings,the cost of retained earnings is generally lower than the after-tax cost of debt.
E) Higher flotation costs tend to reduce the cost of equity capital.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10.1
Assume that you have been hired as a consultant by CGT,a major producer of chemicals and plastics,including plastic grocery bags,styrofoam cups,and fertilizers,to estimate the firm's weighted average cost of capital.The balance sheet and some other information are provided below.
Assets  Liabilities and Equity
Liabilities and Equity 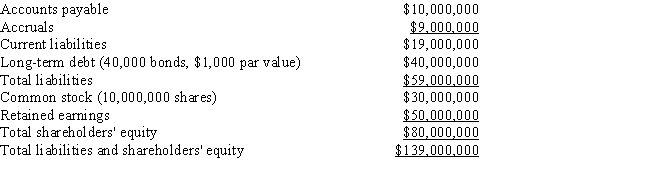 The stock is currently selling for $17.75 per share,and its noncallable $3,319.97 par value,20-year,1.70% bonds with semiannual payments are selling for $881.00.The beta is 1.29,the yield on a 6-month Treasury bill is 3.50%,and the yield on a 20-year Treasury bond is 5.50%.The required return on the stock market is 11.50%,but the market has had an average annual return of 14.50% during the past 5 years.The firm's tax rate is 40%.
-Refer to Exhibit 10.1.Which of the following is the best estimate for the weight of debt for use in calculating the WACC?
The stock is currently selling for $17.75 per share,and its noncallable $3,319.97 par value,20-year,1.70% bonds with semiannual payments are selling for $881.00.The beta is 1.29,the yield on a 6-month Treasury bill is 3.50%,and the yield on a 20-year Treasury bond is 5.50%.The required return on the stock market is 11.50%,but the market has had an average annual return of 14.50% during the past 5 years.The firm's tax rate is 40%.
-Refer to Exhibit 10.1.Which of the following is the best estimate for the weight of debt for use in calculating the WACC?
A) 16.56%
B) 17.23%
C) 17.57%
D) 17.92%
E) 18.64%
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 94
Related Exams