B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The change in net working capital associated with new projects is always positive, because new projects mean that more working capital will be required. This situation is especially true for replacement projects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Any cash flows that can be classified as incremental to a particular project⎯i.e., results directly from the decision to undertake the project⎯should be reflected in the capital budgeting analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following procedures best accounts for the relative risk of a proposed project?
A) Adjusting the discount rate downward if the project is judged to have above-average risk.
B) Reducing the NPV by 10% for risky projects.
C) Picking a risk factor equal to the average discount rate.
D) Ignoring risk because project risk cannot be measured accurately.
E) Adjusting the discount rate upward if the project is judged to have above-average risk.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tallant Technologies is considering two potential projects, X and Y. In assessing the projects' risks, the company estimated the beta of each project versus both the company's other assets and the stock market, and it also conducted thorough scenario and simulation analyses. This research produced the following data: Correlation of the project cash flows with cash flows from currently existing projects. Cash flows are not correlated with the cash flows from existing projects. Cash flows are highly correlated with the cash flows from existing projects.
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
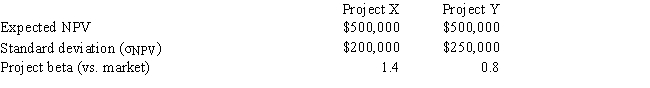
A) Project X has more corporate (or within-firm) risk than Project Y.
B) Project X has more market risk than Project Y.
C) Project X has the same level of corporate risk as Project Y.
D) Project X has less market risk than Project Y.
E) Project X has more stand-alone risk than Project Y.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Sensitivity analysis measures a project's stand-alone risk by showing how much the project's NPV (or IRR) is affected by a small change in one of the input variables, say sales. Other things held constant, with the size of the independent variable graphed on the horizontal axis and the NPV on the vertical axis, the steeper the graph of the relationship line, the more risky the project, other things held constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Under current laws and regulations, corporations must use straight-line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 5 years or longer.
B) Corporations must use the same depreciation method for both stockholder reporting and tax purposes.
C) Using accelerated depreciation rather than straight line normally has the effect of speeding up cash flows and thus increasing a project's forecasted NPV.
D) Using accelerated depreciation rather than straight line normally has no effect on a project's total projected cash flows nor would it affect the timing of those cash flows or the resulting NPV of the project.
E) Since depreciation is a cash expense, the faster an asset is depreciated, the lower the projected NPV from investing in the asset.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DeVault Services recently hired you as a consultant to help with its capital budgeting process. The company is considering a new project whose data are shown below. The equipment that would be used has a 3-year tax life, would be depreciated by the straight-line method over its 3-year life, and would have a zero salvage value. No new working capital would be required. Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 3-year life. What is the project's NPV? 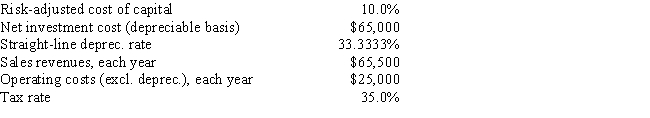
A) $15,740
B) $16,569
C) $17,441
D) $18,359
E) $19,325
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose Walker Publishing Company is considering bringing out a new finance text whose projected revenues include some revenues that will be taken away from another of Walker's books. The lost sales on the older book are a sunk cost and as such should not be considered in the analysis for the new book.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Brandt Enterprises is considering a new project that has a cost of $1,000,000, and the CFO set up the following simple decision tree to show its three most likely scenarios. The firm could arrange with its work force and suppliers to cease operations at the end of Year 1 should it choose to do so, but to obtain this abandonment option, it would have to make a payment to those parties. How much is the option to abandon worth to the firm? 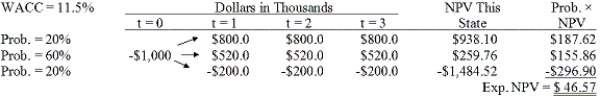
A) $55.08
B) $57.98
C) $61.03
D) $64.08
E) $67.29
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have just landed an internship in the CFO's office of Hawkesworth Inc. Your first task is to estimate the Year 1 cash flow for a project with the following data. What is the Year 1 cash flow? 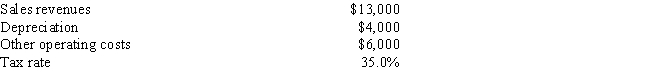
A) $5,950
B) $6,099
C) $6,251
D) $6,407
E) $6,568
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is extremely difficult to estimate the revenues and costs associated with large, complex projects that take several years to develop. This is why subjective judgment is often used for such projects along with discounted cash flow analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fitzgerald Computers is considering a new project whose data are shown below. The required equipment has a 3-year tax life, after which it will be worthless, and it will be depreciated by the straight-line method over 3 years. Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 3-year life. What is the project's Year 1 cash flow? 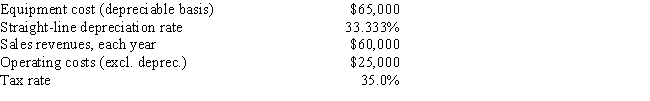
A) $28,115
B) $28,836
C) $29,575
D) $30,333
E) $31,092
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If a firm is found guilty of cannibalization in a court of law, then it is judged to have taken unfair advantage of its customers. Thus, cannibalization is dealt with by society through the antitrust laws.
B) If cannibalization exists, then the cash flows associated with the project must be increased to offset these effects. Otherwise, the calculated NPV will be biased downward.
C) If cannibalization is determined to exist, then this means that the calculated NPV if cannibalization is considered will be higher than the NPV if this effect is not recognized.
D) Cannibalization, as described in the text, is a type of externality that is not against the law, and any harm it causes is done to the firm itself.
E) If a firm is found guilty of cannibalization in a court of law, then it is judged to have taken unfair advantage of its competitors. Thus, cannibalization is dealt with by society through the antitrust laws.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Garden-Grow Products is considering a new investment whose data are shown below. The equipment would be depreciated on a straight-line basis over the project's 3-year life, would have a zero salvage value, and would require some additional working capital that would be recovered at the end of the project's life. Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's life. What is the project's NPV? (Hint: Cash flows are constant in Years 1 to 3.) 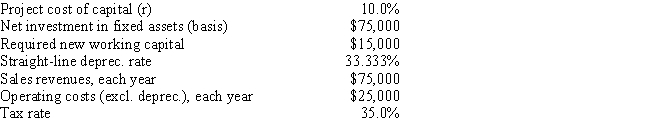
A) $23,852
B) $25,045
C) $26,297
D) $27,612
E) $28,993
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When evaluating a new project, firms should include in the projected cash flows all of the following EXCEPT:
A) Previous expenditures associated with a market test to determine the feasibility of the project, provided those costs have been expensed for tax purposes.
B) The value of a building owned by the firm that will be used for this project.
C) A decline in the sales of an existing product, provided that decline is directly attributable to this project.
D) The salvage value of assets used for the project that will be recovered at the end of the project's life.
E) Changes in net working capital attributable to the project.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sylvester Media is analyzing an average-risk project, and the following data have been developed. Unit sales will be constant, but the sales price should increase with inflation. Fixed costs will also be constant, but variable costs should rise with inflation. The project should last for 3 years, it will be depreciated on a straight-line basis, and there will be no salvage value. This is just one of many projects for the firm, so any losses can be used to offset gains on other firm projects. The marketing manager does not think it is necessary to adjust for inflation since both the sales price and the variable costs will rise at the same rate, but the CFO thinks an adjustment is required. What is the difference in the expected NPV if the inflation adjustment is made vs. if it is not made? 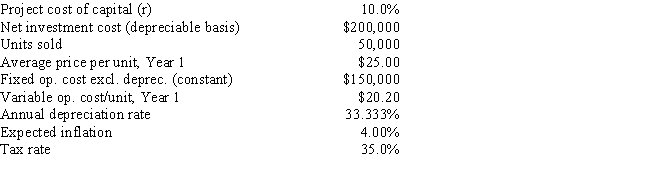
A) $13,286
B) $13,985
C) $14,721
D) $15,457
E) $16,230
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Sunk costs must be considered if the IRR method is used but not if the firm relies on the NPV method.
B) A good example of a sunk cost is a situation where a bank opens a new office, and that new office leads to a decline in deposits of the bank's other offices.
C) A good example of a sunk cost is money that a banking corporation spent last year to investigate the site for a new office, then expensed that cost for tax purposes, and now is deciding whether to go forward with the project.
D) If sunk costs are considered and reflected in a project's cash flows, then the project's calculated NPV will be higher than it otherwise would be.
E) An example of a sunk cost is the cost associated with restoring the site of a strip mine once the ore has been depleted.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Under current laws and regulations, corporations must use straight-line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 3 years or longer.
B) If firms use accelerated depreciation, they will write off assets slower than they would under straight-line depreciation, and as a result projects' forecasted NPVs are normally lower than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes.
C) If they use accelerated depreciation, firms can write off assets faster than they could under straight-line depreciation, and as a result projects' forecasted NPVs are normally lower than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes.
D) If they use accelerated depreciation, firms can write off assets faster than they could under straight-line depreciation, and as a result projects' forecasted NPVs are normally higher than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes.
E) Since depreciation is not a cash expense, and since cash flows and not accounting income are the relevant input, depreciation plays no role in capital budgeting.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) An example of an externality is a situation where a bank opens a new office, and that new office causes deposits in the bank's other offices to decline.
B) The NPV method automatically deals correctly with externalities, even if the externalities are not specifically identified, but the IRR method does not. This is another reason to favor the NPV.
C) Both the NPV and IRR methods deal correctly with externalities, even if the externalities are not specifically identified. However, the payback method does not.
D) Identifying an externality can never lead to an increase in the calculated NPV.
E) An externality is a situation where a project would have an adverse effect on some other part of the firm's overall operations. If the project would have a favorable effect on other operations, then this is not an externality.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 78
Related Exams