A) Differential project risk cannot be accounted for by using "risk-adjusted discount rates" because it is highly subjective and difficult to justify. It is better to not risk adjust at all.
B) Other things held constant, if returns on a project are thought to be positively correlated with the returns on other firms in the economy, then the project's NPV will be found using a lower discount rate than would be appropriate if the project's returns were negatively correlated.
C) Monte Carlo simulation uses a computer to generate random sets of inputs, those inputs are then used to determine a trial NPV, and a number of trial NPVs are averaged to find the project's expected NPV. Sensitivity and scenario analyses, on the other hand, require much more information regarding the input variables, including probability distributions and correlations among those variables. This makes it easier to implement a simulation analysis than a scenario or a sensitivity analysis, hence simulation is the most frequently used procedure.
D) DCF techniques were originally developed to value passive investments (stocks and bonds) . However, capital budgeting projects are not passive investments-managers can often take positive actions after the investment has been made that alter the cash flow stream. Opportunities for such actions are called real options. Real options are valuable, but this value is not captured by conventional NPV analysis. Therefore, a project's real options must be considered separately.
E) The firm's corporate, or overall, WACC is used to discount all project cash flows to find the projects' NPVs. Then, depending on how risky different projects are judged to be, the calculated NPVs are scaled up or down to adjust for differential risk.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A firm that bases its capital budgeting decisions on either NPV or IRR will be more likely to accept a given project if it uses accelerated depreciation than if it uses straight-line depreciation,other things being equal.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) One advantage of sensitivity analysis relative to scenario analysis is that it explicitly takes into account the probability of specific effects occurring, whereas scenario analysis cannot account for probabilities.
B) Well-diversified stockholders do not need to consider market risk when determining required rates of return.
C) Market risk is important, but it does not have a direct effect on stock prices because it only affects beta.
D) Simulation analysis is a computerized version of scenario analysis where input variables are selected randomly on the basis of their probability distributions.
E) Sensitivity analysis is a good way to measure market risk because it explicitly takes into account diversification effects.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
McLeod Inc.is considering an investment that has an expected return of 15% and a standard deviation of 10%.What is the investment's coefficient of variation?
A) 0.67
B) 0.73
C) 0.81
D) 0.89
E) 0.98
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Although it is extremely difficult to make accurate forecasts of the revenues that a project will generate,projects' initial outlays and subsequent costs can be forecasted with great accuracy.This is especially true for large product development projects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Sensitivity analysis measures a project's stand-alone risk by showing how much the project's NPV (or IRR)is affected by a small change in one of the input variables,say sales.Other things held constant,with the size of the independent variable graphed on the horizontal axis and the NPV on the vertical axis,the steeper the graph of the relationship line,the more risky the project,other things held constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Laramie Labs uses a risk-adjustment when evaluating projects of different risk.Its overall (composite) WACC is 10%,which reflects the cost of capital for its average asset.Its assets vary widely in risk,and Laramie evaluates low-risk projects with a WACC of 8%,average-risk projects at 10%,and high-risk projects at 12%.The company is considering the following projects: 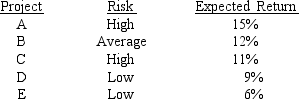 Which set of projects would maximize shareholder wealth?
Which set of projects would maximize shareholder wealth?
A) A and B.
B) A, B, and C.
C) A, B, and D.
D) A, B, C, and D.
E) A, B, C, D, and E.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spot-Free Car Wash is considering a new project whose data are shown below.The equipment to be used has a 3-year tax life,would be depreciated on a straight-line basis over the project's 3-year life,and would have a zero salvage value after Year 3.No new working capital would be required.Revenues and other operating costs will be constant over the project's life,and this is just one of the firm's many projects,so any losses on it can be used to offset profits in other units.If the number of cars washed declined by 40% from the expected level,by how much would the project's NPV decline? (Hint: Note that cash flows are constant at the Year 1 level,whatever that level is.)
A) $28,939
B) $30,462
C) $32,066
D) $33,753
E) $35,530
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following should be considered when a company estimates the cash flows used to analyze a proposed project?
A) Since the firm's director of capital budgeting spent some of her time last year to evaluate the new project, a portion of her salary for that year should be charged to the project's initial cost.
B) The company has spent and expensed $1 million on R&D associated with the new project.
C) The company spent and expensed $10 million on a marketing study before its current analysis regarding whether to accept or reject the project.
D) The firm would borrow all the money used to finance the new project, and the interest on this debt would be $1.5 million per year.
E) The new project is expected to reduce sales of one of the company's existing products by 5%.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) In comparing two projects using sensitivity analysis, the one with the steeper lines would be considered less risky, because a small error in estimating a variable such as unit sales would produce only a small error in the project's NPV.
B) The primary advantage of simulation analysis over scenario analysis is that scenario analysis requires a relatively powerful computer, coupled with an efficient financial planning software package, whereas simulation analysis can be done efficiently using a PC with a spreadsheet program or even with just a calculator.
C) Sensitivity analysis is a type of risk analysis that considers both the sensitivity of NPV to changes in key input variables and the probability of occurrence of these variables' values.
D) As computer technology advances, simulation analysis becomes increasingly obsolete and thus less likely to be used as compared to sensitivity analysis.
E) Sensitivity analysis as it is generally employed is incomplete in that it fails to consider the probability of occurrence of the key input variables.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
We can identify the cash costs and cash inflows to a company that will result from a project.These could be called "direct inflows and outflows," and the net difference is the direct net cash flow.If there are other costs and benefits that do not flow from or to the firm,but to other parties,these are called externalities,and they need not be considered as a part of the capital budgeting analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Taylor Inc.,the company you work for,is considering a new project whose data are shown below.What is the project's Year 1 cash flow?
A) $25,816
B) $27,175
C) $28,534
D) $29,960
E) $31,458
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sheridan Films is considering some new equipment whose data are shown below.The equipment has a 3-year tax life and would be fully depreciated by the straight-line method over 3 years,but it would have a positive pre-tax salvage value at the end of Year 3,when the project would be closed down.Also,some new working capital would be required,but it would be recovered at the end of the project's life.Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 3-year life.What is the project's NPV?
A) $20,762
B) $21,854
C) $23,005
D) $24,155
E) $25,363
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While developing a new product line,Cook Company spent $3 million two years ago to build a plant for a new product.It then decided not to go forward with the project,so the building is available for sale or for a new product.Cook owns the building free and clear-there is no mortgage on it.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If the building could be sold, then the after-tax proceeds that would be generated by any such sale should be charged as a cost to any new project that would use it.
B) This is an example of an externality, because the very existence of the building affects the cash flows for any new project that Rowell might consider.
C) Since the building was built in the past, its cost is a sunk cost and thus need not be considered when new projects are being evaluated, even if it would be used by those new projects.
D) If there is a mortgage loan on the building, then the interest on that loan would have to be charged to any new project that used the building.
E) Since the building has been paid for, it can be used by another project with no additional cost. Therefore, it should not be reflected in the cash flows for any new project.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tallant Technologies is considering two potential projects,X and Y.In assessing the projects' risks,the company estimated the beta of each project versus both the company's other assets and the stock market,and it also conducted thorough scenario and simulation analyses.This research produced the following data:  Correlation of the project cash flows with cash flows from currently existing projects.Cash flows are not correlated with the cash flows from existing projects.Cash flows are highly correlated with the cash flows from existing projects.
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
Correlation of the project cash flows with cash flows from currently existing projects.Cash flows are not correlated with the cash flows from existing projects.Cash flows are highly correlated with the cash flows from existing projects.
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Project X has more corporate (or within-firm) risk than Project Y.
B) Project X has more market risk than Project Y.
C) Project X has the same level of corporate risk as Project Y.
D) Project X has less market risk than Project Y.
E) Project X has more stand-alone risk than Project Y.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Because of differences in the expected returns on different investments,the standard deviation is not always an adequate measure of risk.However,the coefficient of variation adjusts for differences in expected returns and thus allows investors to make better comparisons of investments' stand-alone risk.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors should be included in the cash flows used to estimate a project's NPV?
A) Interest on funds borrowed to help finance the project.
B) The end-of-project recovery of any working capital required to operate the project.
C) Cannibalization effects, but only if those effects increase the project's projected cash flows.
D) Expenditures to date on research and development related to the project, provided those costs have already been expensed for tax purposes.
E) All costs associated with the project that have been incurred prior to the time the analysis is being conducted.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) In a capital budgeting analysis where part of the funds used to finance the project would be raised as debt, failure to include interest expense as a cost when determining the project's cash flows will lead to a downward bias in the NPV.
B) The existence of any type of "externality" will reduce the calculated NPV versus the NPV that would exist without the externality.
C) If one of the assets to be used by a potential project is already owned by the firm, and if that asset could be sold or leased to another firm if the new project were not undertaken, then the net after-tax proceeds that could be obtained should be charged as a cost to the project under consideration.
D) If one of the assets to be used by a potential project is already owned by the firm but is not being used, then any costs associated with that asset is a sunk cost and should be ignored.
E) In a capital budgeting analysis where part of the funds used to finance the project would be raised as debt, failure to include interest expense as a cost when determining the project's cash flows will lead to an upward bias in the NPV.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have just landed an internship in the CFO's office of Hawkesworth Inc.Your first task is to estimate the Year 1 cash flow for a project with the following data.What is the Year 1 cash flow? Srles reyenues Depreciation Other aperating casts Tax rate
A) $5,950
B) $6,099
C) $6,251
D) $6,407
E) $6,568
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following rules is CORRECT for capital budgeting analysis?
A) Only incremental cash flows, which are the cash flows that would result if a project is accepted, are relevant when making accept/reject decisions.
B) Sunk costs are not included in the annual cash flows, but they must be deducted from the PV of the project's other costs when reaching the accept/reject decision.
C) A proposed project's estimated net income as determined by the firm's accountants, using generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) , is discounted at the WACC, and if the PV of this income stream exceeds the project's cost, the project should be accepted.
D) If a product is competitive with some of the firm's other products, this fact should be incorporated into the estimate of the relevant cash flows. However, if the new product is complementary to some of the firm's other products, this fact need not be reflected in the analysis.
E) The interest paid on funds borrowed to finance a project must be included in estimates of the project's cash flows.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 78
Related Exams