A) Adult Hb binds to oxygen more tightly than Mb binds.
B) Fetal Hb binds oxygen more tightly than adult Hb.
C) Adult Hb binds oxygen more tightly than either fetal Hb or Mb binds.
D) Mb has the lowest affinity for oxygen of the 3.
E) More than one of these statements is correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding hydrogen bonding in secondary structures is true ?
A) Both α -helices and β -sheets only use intrachain hydrogen bonds.
B) Both α -helices and β -sheets only use interchain hydrogen bonds.
C) α -helices only use intrachain hydrogen bonds and β -sheets can use either intrachain or interchain hydrogen bonds.
D) α -helices can use either intrachain or interchain hydrogen bonds and β -sheets only use interchain hydrogen bonds.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 4A The following question(s) refer to this peptide: Cys-Ala-Gly-Arg-Gln-Met Refer to Exhibit 4A. The carboxyl terminal end is:
A) Arg
B) Cys
C) Gln
D) Met
E) None of these.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) The peptide bonds in the β -sheet are extended.
B) The peptide bonds in the α -helix coil back on themselves.
C) Both α -helices and β -sheets can be found as part of tertiary structure.
D) All of these
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 4B 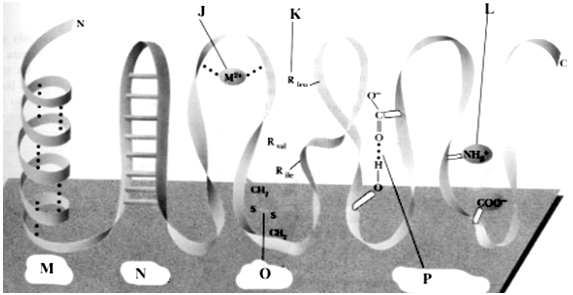 Refer to Exhibit 4B. The type of bonding labeled "N" in these figure is:
Refer to Exhibit 4B. The type of bonding labeled "N" in these figure is:
A) Hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone
B) Covalent bonding involving the R-groups
C) Hydrophobic interactions
D) Metal ion coordination
E) Electrostatic attraction
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best defines a domain?
A) A supersecondary region, often shared by proteins, that has a specific function.
B) A repetitive supersecondary structure.
C) A double-layered arrangement formed so that the polar groups face the aqueous environment, while the nonpolar regions are kept away from the aqueous environment.
D) An unfolded region of a protein.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In allosteric interactions
A) proteins that consist of a single polypeptide chain form aggregates.
B) disulfide bonds are broken.
C) changes that take place in one site of a protein cause changes at a distant site.
D) metal ions always bind to the protein.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The tertiary structure of a protein is usually a result of which of the following interactions?
A) intramolecular hydrogen bonding
B) electrostatic interactions
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) all of these
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following is true about the hydroxyproline in collagen:
A) Hydroxyproline is incorporated into the chain during polymerization of amino acids.
B) Vitamin C is necessary for the synthesis of hydroxyproline.
C) Hydroxyproline is important in holding the 3 strands of collagen together.
D) Hydroxyproline requires Vitamin C for its synthesis and it holds the collagen helix together.
E) All of these.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 4A The following question(s) refer to this peptide: Cys-Ala-Gly-Arg-Gln-Met Refer to Exhibit 4A. The amino terminal amino acid is:
A) Arg
B) Cys
C) Gln
D) Met
E) None of these.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following bond forces are important in tertiary structure:
A) Disulfide bonds
B) Hydrogen bonds
C) Hydrophobic attraction
D) Both hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic attraction.
E) All of these are important in tertiary structure
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following proteins is not homologous with the others?
A) myoglogin
B) α -chain of hemoglobin
C) β -chain of hemoglobin
D) collagen
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The oxygen binding curve of which of the following is the closest to that of myoglobin?
A) hemoglobin at pH 6.8
B) hemoglobin that lacks BPG
C) maternal hemoglobin
D) fetal hemoglobin
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bohr effect for oxygen binding states that
A) Mb binds oxygen more tightly than Hb.
B) Hb will bind oxygen very tightly when the CO2 concentration is high.
C) as the pH goes down, Hb binds oxygen less tightly.
D) Hb's ability to bind oxygen increases with higher oxygen concentration.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding hemoglobin (Hb) and myoglobin (Mb) is true?
A) Mb transports oxygen while Hb stores it.
B) Mb has quaternary structure but Hb does not.
C) Mb displays simple kinetics of binding while Hb displays cooperativity.
D) Mb binds Fe(II) while Hb binds heme.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_____ are natural glycoproteins found in the cell membranes of nerve tissues and are known to cause spongiform encephalopathy in humans.
A) Viroids
B) Actin-binding proteins
C) Alpha-fetoproteins
D) Prions
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the portion of proteins that does not consist of amino acids.
A) Subunit
B) Prosthetic group
C) Domain
D) Motif
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following bond forces are important in quaternary structure:
A) Disulfide bonds
B) Hydrogen bonds
C) Hydrophobic attraction
D) Both hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic attraction.
E) All of these are important in quaternary structure.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes a motif?
A) a repetitive supersecondary structure
B) a common nonrepetitive irregularity found in antiparallel β -sheets
C) a protein conformation with biological activity
D) a group of atoms other than an amino acid
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one is not an example of supersecondary structure?
A) the pyrrole ring
B) the Greek key
C) the β -meander
D) the β -barrel
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 87
Related Exams