A) A service that provides temporary secretaries to companies
B) An automobile factory
C) A farm
D) An electric utility
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely to be a fixed cost for farmer McDonald? Fertilizer
A) Gasoline
B) Fertilizer
C) Insurance
D) Seed
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following indicates an input is being overused relative to the optimal level?
A) MRP = P of input.
B) MRP > P of input.
C) MRP < P of input.
D) MPP > P of output.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm's optimal input proportions may change if
A) input prices change.
B) the relative marginal productivities of the inputs change.
C) the firm's optimal output level changes.
D) All of the responses are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-7 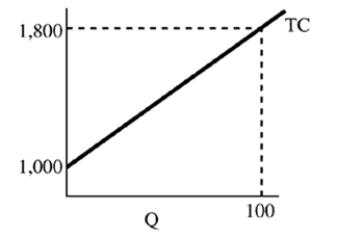 -In Figure 7-7 at 100 units, AVC equals
-In Figure 7-7 at 100 units, AVC equals
A) 8.
B) 800.
C) 100.
D) 1,000.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The principal determinants of total and average cost curves are the firm's technology and the prices of its inputs.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cost minimization requires that a firm equate the ratio of marginal products of inputs to the ratio of input prices.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Decreasing returns to scale is strictly a short run phenomenon for firms.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economies of scale
A) require inputs' MPP to fall as output increases (everything else equal) .
B) pertain to the long run only.
C) refer to increased output generalized by an increase in the quantity of a single input.
D) imply that the AC curve will fall continuously as output increases in the short run.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run,
A) all of the firm's input quantities are variable.
B) the firm can vary the quantities of some but not all inputs.
C) managers become less efficient.
D) the total cost of producing any given level of output is greater than or equal to the short-run total cost of producing that level of output.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The marginal cost curve shows the per-unit cost associated with various levels of output.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-10 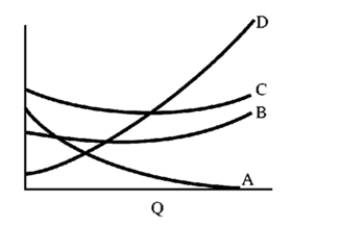 -The typical average cost curve
-The typical average cost curve
A) continually declines as output increases.
B) is horizontal.
C) continually increases as output increases.
D) first declines to a minimum and then increases as output increases.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal cost is the
A) change in total cost resulting from the purchase of one more unit of the variable input.
B) change in total cost resulting from the production of one more unit of output.
C) difference between total fixed cost and total variable cost.
D) difference between total cost and total expenditure.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economies of scale is another term for
A) increasing returns to scale.
B) constant returns to scale.
C) increasing marginal physical productivity.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following equations defines marginal revenue product?
A) MRP = P times Q.
B) MRP = total cost.
C) MRP = total revenue minus total cost.
D) MRP = MPP times price of the product.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where marginal cost is less than average cost,
A) opportunity cost must have been excluded from the calculation of marginal cost.
B) marginal cost must be falling.
C) marginal cost must be rising.
D) marginal cost may be rising, falling, or constant.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-15 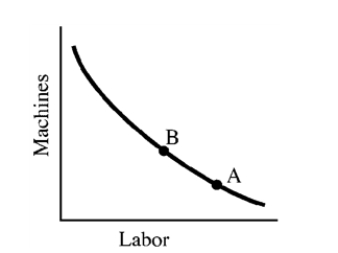 -For a firm at equilibrium, at point A in Figure 7-15,
-For a firm at equilibrium, at point A in Figure 7-15,
A) the price of labor is high relative to the price of machines.
B) the MPP of labor is greater than the MPP of machines.
C) the MPP of labor is less than at point B.
D) output is higher than at point B.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm's marginal physical product is 5, and it sells its product for $60, and a unit of labor costs $200, the firm should
A) increase the use of labor.
B) decrease the use of labor.
C) decrease the price of the product.
D) reduce output of the product.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following observations is true?
A) In the long run, more costs become variable.
B) Fixed costs cannot be completely varied if the time period is sufficiently long.
C) Fixed costs arise when some types of inputs can be bought only in big batches.
D) Variable costs arise when inputs have a large productive capacity.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph of the average cost curve
A) is identical to the AVC curve.
B) is above the AVC curve
C) lies everywhere below the AFC curve.
D) lies below the AFC curve.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 246
Related Exams