B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Synthesis of a repressible enzyme is stopped by the
A) substrate binding to the repressor.
B) corepressor-repressor complex binding to the operator.
C) corepressor binding to the operator.
D) allosteric transition.
E) end product binding to the promoter.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The miRNAs in a cell
A) are responsible for inducing operons.
B) are a part of the eukaryotic ribosome.
C) allow different cells to produce different proteins.
D) are a part of the prokaryotic ribosome.
E) are found in prokaryotic cells.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 8.3 - Metabolic Pathway -In Figure 8.3, if enzyme A is an inducible enzyme,
A) compound B would bind to enzyme A directly.
B) compound C would react with gene a directly.
C) compound C would bind to the repressor for Gene a.
D) compound A would react with enzyme B directly.
E) compound A would bind to the repressor for Gene a.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 8.2
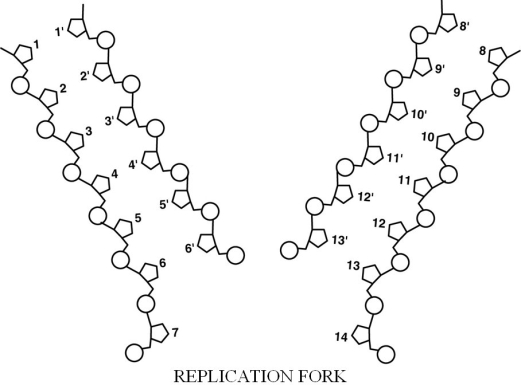 -In Figure 8.2, base 2 (and ONLY the base) is covalently bound/attached to
-In Figure 8.2, base 2 (and ONLY the base) is covalently bound/attached to
A) deoxyribose.
B) phosphate.
C) thymine.
D) ribose.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 8.2 Codon on mRNA and corresponding amino acid -Refer to Table 8.2. What is the sequence of amino acids encoded by the following sequence of bases in a strand of DNA (pay attention to the polarity of the DNA here) ? 3? ATTACGCTTTGC
A) Translation would stop at the first codon.
B) asparagine-arginine-lysine-alanine
C) asparagine-cysteine-valine-serine
D) leucine-arginine-lysine-alanine
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a product of transcription?
A) rRNA
B) a new strand of DNA
C) tRNA
D) mRNA
E) None of the answers are correct; all of these are products of transcription.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Recombination will always alter a cellʹs genotype.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Transposition (insertion of a transposon into a DNA sequence) results in the formation of base substitution mutations in a cellʹs DNA.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the operon model, for the synthesis of an inducible enzyme to occur, the
A) repressor must bind to the operator.
B) end-product must not be in excess.
C) substrate must bind to the enzyme.
D) repressor must not be synthesized.
E) substrate must bind to the repressor.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme that makes covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate groups in another nucleotide in DNA is
A) RNA polymerase.
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA helicase.
D) transposase.
E) DNA polymerase.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The miRNAs in a cell inhibit protein synthesis by forming complementary bonds with rRNA.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 8.2
 -In Figure 8.2, if base 4 is thymine, what is base 4ʹ?
-In Figure 8.2, if base 4 is thymine, what is base 4ʹ?
A) guanine
B) adenine
C) cytosine
D) thymine
E) uracil
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mutations that are harmful to cells occur more frequently than those that benefit cells.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the Ames test, any colonies that form on the control should be the result of spontaneous mutations.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The initial effect of ionizing radiation on a cell is that it causes
A) DNA to break.
B) base substitutions.
C) the formation of highly reactive ions.
D) bonding between adjacent thymines.
E) the cells to get hot.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme that catalyzes the cutting and resealing of DNA, and is translated from insertion sequences, is
A) RNA polymerase.
B) DNA ligase.
C) DNA helicase.
D) transposase.
E) DNA polymerase.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 8.4 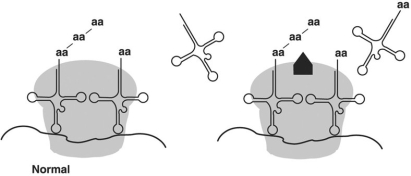 In Figure 8.4, the antibiotic chloramphenicol binds the 50S large subunit of a ribosome as shown (the light gray area is the large subunit, while the black shape is the drug) . From this information you can conclude that chloramphenicol
In Figure 8.4, the antibiotic chloramphenicol binds the 50S large subunit of a ribosome as shown (the light gray area is the large subunit, while the black shape is the drug) . From this information you can conclude that chloramphenicol
A) prevents translation in eukaryotes.
B) prevents translation in prokaryotes.
C) prevents transcription in eukaryotes.
D) prevents mRNA-ribosome binding.
E) prevents transcription in prokaryotes.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Conjugation differs from reproduction because conjugation
A) transcribes DNA to RNA.
B) replicates DNA.
C) transfers DNA vertically, to new cells.
D) copies RNA to make DNA.
E) transfers DNA horizontally, to nearby cells without those cells undergoing replication.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 8.3 - Metabolic Pathway -In Figure 8.3, if compound C reacts with the allosteric site of enzyme A, this would exemplify
A) competitive inhibition.
B) transcription.
C) feedback inhibition.
D) a mutation.
E) repression.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 48
Related Exams