A) G₁
B) S
C) G₂
D) G₀
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly synthesized DNA and, therefore, can be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student-faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into a culture of dividing human cells at specific times. Which of the following questions might be answered by using the method described?
A) How many cells are produced by the culture per hour?
B) What is the length of the S phase of the cell cycle?
C) How many picograms of DNA are made per cell cycle?
D) When do spindle fibers attach to chromosomes?
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a cell at metaphase of mitosis contains 20 sister chromatids, how many chromosomes will be present in a G₁ cell?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and, therefore, can be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student-faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides to study the incorporation of labeled nucleotides into a culture of lymphocytes. They found that the lymphocytes incorporated the labeled nucleotide at a significantly higher level after a pathogen was introduced into the culture. What might they conclude from this observation?
A) The pathogen consumed radiolabeled nucleotides.
B) Infection causes lymphocytes to divide more rapidly.
C) Infection causes lymphocytes to increase in size.
D) Infection causes lymphocyte cultures to skip some parts of the cell cycle.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the question below.
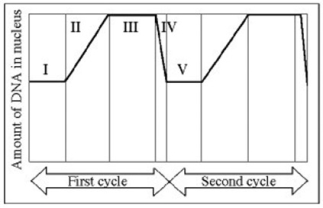 In the figure, MPF reaches its highest concentration during this stage.
In the figure, MPF reaches its highest concentration during this stage.
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following properties is associated with a cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) ?
A) A Cdk is inactive, or "turned off," in the presence of a cyclin.
B) The number of Cdk molecules increases during the S and G₂ phases and decrease during M.
C) A Cdk is an enzyme that catalyzes the attachment of kinetochores to microtubules.
D) A Cdk is an enzyme that attaches phosphate groups to other proteins.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a diploid cell with 5 chromosome pairs (2n = 10) , how many sister chromatids will be found in a nucleus at prophase of mitosis?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One difference between cancer cells and normal cells is that cancer cells
A) are unable to synthesize DNA.
B) are arrested at the S phase of the cell cycle.
C) continue to divide even when they are tightly packed together.
D) cannot function properly because they are affected by density-dependent inhibition.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The M phase checkpoint ensures that all chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. If this does not happen, cells would most likely be arrested in ________.
A) telophase
B) prophase
C) G₂
D) metaphase
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mitotic spindle plays a critical role in which of the following processes?
A) splitting of the cell (cytokinesis) following mitosis
B) triggering the compaction and condensation of chromosomes
C) dissolving the nuclear membrane
D) separation of sister chromatids
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At which phase of the cell cycle do centrioles begin to move apart in animal cells?
A) anaphase
B) telophase
C) metaphase
D) prophase
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the animal cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B?
A) spindle formation
B) spindle attachment to kinetochores
C) cell elongation during anaphase
D) cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the question below.
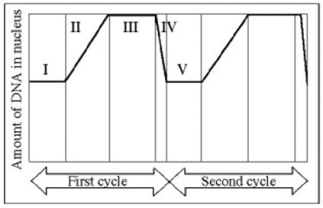 In the figure, which number represents DNA synthesis?
In the figure, which number represents DNA synthesis?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the microtubule-organizing center found in animal cells as an identifiable structure present during all phases of the cell cycle?
A) centriole
B) centrosome
C) centromere
D) kinetochore
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not occur during mitosis?
A) condensation of the chromosomes
B) replication of the DNA
C) separation of sister chromatids
D) spindle formation
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the question below.
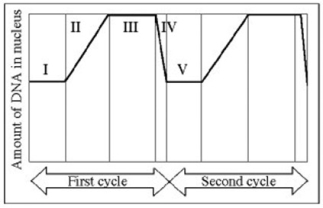 In the figure, at which of the numbered regions would you expect to find cells at metaphase?
In the figure, at which of the numbered regions would you expect to find cells at metaphase?
A) II and IV
B) II only
C) III only
D) IV only
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote) , a series of six cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how many cells?
A) 12
B) 16
C) 32
D) 64
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exposure of zebrafish nuclei to cytosol isolated from eggs at metaphase of mitosis resulted in phosphorylation of NEP55 and L68 proteins by cyclin-dependent kinase 2. NEP55 is a protein of the inner nuclear membrane, and L68 is a protein of the nuclear lamina. What is the most likely role of phosphorylation of these proteins in the process of mitosis?
A) They enable the attachment of the spindle microtubules to kinetochore regions of the centromere.
B) They are involved in chromosome condensation.
C) They are involved in the disassembly of the nuclear envelope.
D) They assist in the migration of centrosomes to opposite sides of the nucleus.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Density-dependent inhibition is explained by which of the following processes?
A) As cells become more numerous, they begin to squeeze against each other, restricting their size.
B) As cells become more numerous, the cell surface proteins of one cell contact the adjoining cells, and they signal each other to stop dividing.
C) As cells become more numerous, the protein kinases they produce begin to compete with each other, such that the proteins produced by one cell essentially cancel those produced by its neighbor.
D) As cells become more numerous, the level of waste products increases, which slows metabolism and inhibits growth.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Metaphase is characterized by ________.
A) alignment of chromosomes on the equator of the cell
B) separation of the centromeres
C) cytokinesis
D) separation of sister chromatids
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 66
Related Exams