Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange H2S,H2Se,and H2Te in order from lowest to highest boiling point.
A) H2Te < H2Se < H2S
B) H2S < H2Se < H2Te
C) H2S < H2Te < H2Se
D) H2Se < H2Te < H2S
E) H2Te < H2S < H2Se
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules has the lowest boiling point?
A) CH4
B) CHCl3
C) CH2Cl2
D) CH3Cl
E) CCl4
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At 80.0 °C,water has an equilibrium vapor pressure of 355.1 mm Hg.If 4.22 g H2O is sealed in an evacuated 5.00 L flask and heated to 80.0 °C,what mass of H2O will be found in the gas phase when liquid-vapor equilibrium is established? Assume any liquid remaining in the flask has a negligible volume.(R = 0.08206 L⋅atm/mol⋅K,1 atm = 760 mm Hg)
A) 0.689 g
B) 1.45 g
C) 1.67 g
D) 2.77 g
E) 4.22 g
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capillary action is ____
A) resistance to flow.
B) the rate of collisions for gas molecules.
C) the energy required to overcome the attractive forces between molecules in the liquid state to form a gas.
D) the force required to expand the surface of a liquid.
E) the drawing of a liquid up the inside of a small-bore tube when adhesive forces exceed cohesive forces.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes what happens when a small amount of solid potassium chloride is dissolved in water?
A) The heat from the warm water melts the solid,making it a liquid.
B) Nothing happens,because potassium chloride is insoluble in water.
C) The solid KCl breaks apart into separate K and Cl atoms by interacting with the water molecules.
D) The water molecules surround each ion in the solid KCl,separating the K ions from the Cl ions.
E) The solid undergoes a chemical change by reacting with the water.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
________ is a measure of the degree to which the electron cloud surrounding an atom or molecule can be distorted in an electric field.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ammonia (NH3) is used as a refrigerant.At its boiling point of -33 °C,the standard enthalpy of vaporization of ammonia is 23.3 kJ/mol.How much heat is released when 50.0 g of ammonia is condensed at -33 °C?
A) -0.466 kJ
B) -7.94 kJ
C) -36.6 × 103 kJ
D) -68.4 kJ
E) -1.17 × 103 kJ
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Normal boiling point is defined as
A) the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals 1 atm.
B) the pressure at which any liquid boils at 373.15 K.
C) the temperature at which water boils in a vacuum.
D) the temperature at which the liquid and gaseous phases of a substance have equal densities.
E) the temperature at which the enthalpy of vaporization equals 100.0 kJ/mol.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic of volatile liquids?
A) Volatile liquids are easily vaporized.
B) Volatile liquids have relatively high vapor pressures.
C) Volatile liquids have strong cohesive forces.
D) Volatile liquids have weak intermolecular forces.
E) All of these
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange HF,HCl,and HBr in increasing order of their boiling point.
A) HF < HCl < HBr
B) HF < HBr < HCl
C) HBr < HF < HCl
D) HBr < HCl < HF
E) HCl < HBr < HF
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules has the highest enthalpy of vaporization?
A) N2
B) O2
C) I2
D) CH4
E) C6H6
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following molecules will exhibit dipole-dipole intermolecular forces as a pure liquid or solid?
A) CSe2
B) C2H2
C) SiF4
D) O2
E) PF3
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following intermolecular forces or bonds is primarily responsible for the solubility of argon (Ar) in water?
A) Dipole-dipole force
B) Hydrogen bonding
C) Dipole-induced dipole force
D) Hydrogen bonding-dipole force
E) Ion-induced dipole force
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following nonpolar molecules has the highest boiling point?
A) N2
B) C2H4
C) F2
D) O2
E) CS2
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrogen bonding is present in all of the following molecular solids EXCEPT ____.
A) H2SO4 (dihydrogen sulfate)
B) CH3OH (methanol)
C) CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether)
D) HF (hydrogen fluoride)
E) CH3CO2H (acetic acid)
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which intermolecular force or bond is responsible for the density of H2O(s) being less than that of H2O( 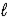 ) ?
) ?
A) London dispersion forces
B) hydrogen bonding
C) ionic bonding
D) covalent bonding
E) dipole/induced dipole forces
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following compounds has a boiling point closest to that of argon?
A) F2
B) Cl2
C) HCl
D) NaF
E) HF
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The vapor pressure of a given liquid will increase if
A) the liquid is moved to a container in which its surface area is very much larger.
B) the volume of the liquid is increased.
C) the temperature is increased.
D) the volume of the vapor phase is increased.
E) a more volatile liquid is added to the given liquid.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following strong electrolytes has the most negative hydration enthalpy?
A) NaCl
B) KCl
C) RbCl
D) CsCl
E) HCl
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 69
Related Exams